PC power supply is, in many cases, attached just
like an "accessory of chassis" when chassis is bought.
In reality, it's no exaggeration to say that it is the most critical
part of PC.
Because, to tell the work of PC mentioned above in one word, it
is "to convert AC delivered to household and stably provide
computer devices such as a motherboard" with DC (direct current).
If it becomes unstable or broken, all functions get crashed to lose
important data.
Is PC power supply special? No, No. In fact, many home appliances
have power supply inside to convert AC to DC. Commonly seen AC adapter,
for example, is externally placed type of built-in power supply.
In daily life, we are not conscious of power supply of home appliances
as it is built in them, and home appliances have no need to replace
power supply because of no expandability of them.
Also, you cannot find out power supply for TV set at shops even
when you want to replace. On the contrary, you may possibly replace
PC power supply as PC has expandability to add HDD or replace CPU.
Power supply is originally limited life component so that you need
to replace at some stage.
<< Category and Differences of PC power supplies
>>
PC power supplies are categorized mainly into 4 types,
such as AT power supply, ATX power supply, SFX power supply,
and EPS power supply. Almost every PC power supply at shops
is ATX type. AT and SFX type is not so large. There are other
type power supply for NLX or WTX too, but they are built-in
in the chassis so that you can hardly get them individually.
ATX type provides you a wide range to choose from as there
are many motherboards. SFX power supply is for microATX motherboard.
AT type's application is getting limited mainly for FA (Factory
Automation), but, as mentioned later, it is still used due
to stable ON/OFF control of power supply. In addition, there
are ATX12V・SFX12V specification as successor to ATX/SFX specification
and, they are compatible with previous specifications. (-5V
is not required for ATX12V). Now, let us explain the differences
among PC power supplies.
|

Photo 2.1
AT type bottom left
ATX type bottom right
SFX type in the center
5 dimensions for SFX power supply are offered so that you
need to verify if it fits to chassis even with the same SFX
specification. Outlet is provied to AT power supply.
|
First, take a look at dimension. AT type and ATX type have the
dimension called PS/2 size. They may look identical. On the other
hand, SFX type is less than 50% as small as PS/2 in volume. (Photo
2.1)
Each PC power supply has various shapes of main connector to be
connected to motherboard and output voltages. This is because type
of motherboard requires different voltages as shown in Table 2.1.
Table 2.1 Main connector to supply power to
motherboard
| Category |
AT
power supply |
ATX
power supply |
ATX12V
power supply |
SFX
power supply |
ATX12V
power supply |
| Connector shape |
6 pin
2 pcs. |
20 pin
1 pc. |
24 pin
1 pc. |
20 pin
1 pc.
|
24 pin
1 pc. |
| Size (WxDxH) |
150x140x86 |
150x140x86 |
100x125x63.5 |
| Output voltage |
+5V, +12V, -5V, -12V |
+3.3V, +5V, +12V, (-5V), -12V, +5VSB
* -5V is optional for ATX12V |
+3.3V, +5V, +12V, (-5V), -12V, +5VSB
* -5V is optional |
+5VSB is always on for ATX and SFX type when AC
is turned on.
This output is used to control power supply startup,
and to provide power to Wake ON LAN, Wake ON Modem Ring.
Ref. 1: Pinout assignment of main 20Pin
connector for ATX type
Pin |
Output |
Output |
Pin |
11 |
3.3V |
3.3V |
1 |
12 |
-12V |
3.3V |
2 |
13 |
COM |
COM |
3 |
14 |
PS_ON |
5V |
4 |
15 |
COM |
COM |
5 |
16 |
COM |
5V |
6 |
17 |
COM |
COM |
7 |
18 |
-5V |
PWR_OK |
8 |
19 |
5V |
5VSB |
9 |
20 |
5V |
12V |
10 |
* COM is zero volt level of secondary output.
* For PS_ON, all outputs turn ON when this pin is activated by TTL
Low.
* PWR_OK delivers TTL High (approx. 5V) when outputs become stable.
* -5V is optional for SFX type.
Ref. 2: Pinout assignment of main connector
6Pin 2 pcs. for AT type
Pin1 |
Output |
1 |
P.G. |
2 |
+5V |
3 |
+12V |
4 |
-12V |
5 |
COM |
6 |
COM |
|
Pin2 |
Output |
1 |
COM |
2 |
COM |
3 |
-5V |
4 |
+5V |
5 |
+5V |
6 |
+5V |
|
* P.G. is the same signal as PWR_OK of ATX type.
Ref. 3: Pinout assignment of peripheral
connector and FDD connector
Pinout assignment of peripheral connector
Pin1 |
Output |
1 |
+12V |
2 |
COM |
3 |
COM |
4 |
+5V |
|
Pinout assignment of FDD connector
Pin2 |
Output |
1 |
+5V |
2 |
COM |
3 |
COM |
4 |
+12V |
|
* P.G. is the same signal as PWR_OK of ATX type.
Ref. 4: Pinout assignment of main 24Pin
connector for ATX12V type
Pin |
Output |
Output |
Pin |
13 |
3.3V |
3.3V |
1 |
14 |
-12V |
3.3V |
2 |
15 |
COM |
COM |
3 |
16 |
PS_ON |
5V |
4 |
17 |
COM |
COM |
5 |
18 |
COM |
5V |
6 |
19 |
COM |
COM |
7 |
20 |
-5V |
PWR_OK |
8 |
21 |
5V |
5VSB |
9 |
22 |
5V |
12V |
10 |
23 |
5V |
12V |
11 |
24 |
COM |
3.3V |
12 |
* COM is zero volt level of secondary output.
* For PS_ON, all outputs turn ON when this pin is activated by TTL
Low.
* PWR_OK delivers TTL High (approx. 5V) when outputs become stable.
Ref. 5:Pinout assignment of 12V Power Connector
and 6Pin connector for PCI-Express
Pinout assignment of Power Connector for +12V
|
Pin1 |
Output |
1 |
COM |
2 |
COM |
3 |
+12V |
4 |
+12V |
|
Pinout assignment of 6Pin connector for PCI-Express
Pin2 |
Output |
1 |
+12V |
2 |
+12V |
3 |
+12V |
4 |
COM |
5 |
COM |
6 |
COM |
|
Ref. 6: Pinout assignment of 8Pin Processor
Power Connector
Pin |
Output |
Output |
Pin |
1 |
COM |
+12V |
5 |
2 |
COM |
+12V |
6 |
3 |
COM |
+12V |
7 |
4 |
COM |
+12V |
8 |
AT and ATX power supply are dimensionally identical, but there
are much difference in its shape and output power to be recognized.
Also, ATX power supply includes outputs of SFX power supply and
its connector shape is the same.
For this reason, ATX power supply is available to mother-board of
microATX. PC power supply is equipped with peripheral connector
(large 4Pin connector) and FDD connector (small 4Pin connector)
other than main connector. The shape and output voltages are the
same despite the difference of number of connectors. (Photo 2.2
and 2.3)
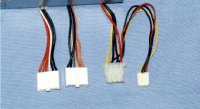
Photo 2.2 Connectors of ATX type
From left, main connectors (6Pin 2 pcs.), Peripheral connector,
and FDD connector |
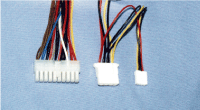
Photo 2.3 Connectors of ATX and SFX type
From left, main connector (20Pin 1pc.), Peripheral connector,
and FDD connector |
Moreover, regarding ON/OFF control, it is categorized into
2 types.
One is ATX power supply which needs manual operation, second,
ATX and SFX power supply which can be controlled by motherboard.
Faston terminals are normally equipped to AT power supply
(Photo 2.4).
It allows power supply to turn on or off by operating external
switch. In the case that outlet is equipped for monitor connection,
ON/OFF of monitor can be controlled in conjunction with PC
operation.
In addition, ON/OFF control of PC is secured while it does
not depend on PC condition as supply mains can be turned on
or off manually.
On the contrary, for ATX and SFX power supply, ON/OFF control
is carried out by electric control from motherboard, voltage
of control terminal of main connector, pin 14, to be exact.
(Photo 2.5)
When TTL Low (same voltage as black cable that is zero volt)
is given, PC becomes activated.
When PC with ATX specification is started up, a switch on
the front panel is usually pressed down. In this operation,
supply mains of PC power supply is not directly turned on,
but a signal is given to mother-board to turn on PC power
supply indirectly.
Also, this control allows the function to shut down automatically
PC power supply when OS of Windows2000/XP shuts down (Figure
2.3). AT power supply has the advantage of fail-safe operation
over ON/OFF control method that depends on motherboard. Fail-safe
means that the nit operates to safe side when abnormal situation
occurs. This is why AT power supply is adopted for FA use. |
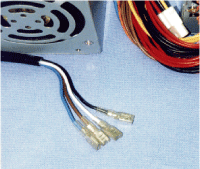
Photo 2.4 Faston terminals of AT power supply Connect a switch
to those to turn on or off power supply manually.
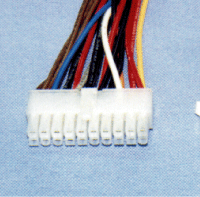
Photo 2.5 Pin 14 of main connector of 20Pin is for ON/OFF
control.
|
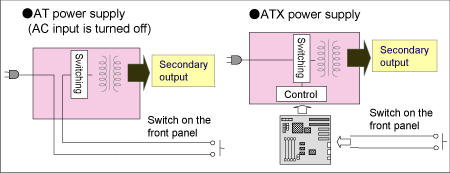
Fig 2.3 For AT power supply, ON/OFF of PC
power supply is controlled manually.
For ATX and SFX power supply, ON/OFF of PC power supply is controlled
by signal from motherboard.
<< How to start up ATX power supply >>
Starting up ATX power supply by itself without connecting to motherboard
can be carried out by giving pseudo signal.
This is useful to see where the problem that the unit does not start
up comes from, power supply itself? or motherboard?
To make pseudo signal, turn PS_ON of main connector to TTL Low,
or connect PS_ON to COM, providing that minimum load is given.
This is because just one transformer in PC power supply handles
multiple outputs. Some units may not deliver 3.3V or 12V when 5V
does not have approx. 2A of load.
Without any load, proper output may not be delivered when ON operation
of power supply is carried out. Make sure to give minimum load.
Many of our products can operate normally even with no load (zero
amps.).
<< Is power supply which differs from the
specification of motherboard acceptable? >>
Some may wonder "ATX power supply is acceptable to motherboard
of AT?" The answer is "YES."
Table 2.2 below shows the combination of different power supplies
and motherboards to see what will happen.
Table 2.2 Cross combination of power supplies
and motherboards
|
MB/PSU |
AT
power supply |
ATX
power supply |
SFX
power supply |
EPS
power supply |
AT |
OK |
Conversion connector required |
Conversion connector required |
Conversion connector required |
ATX |
Unacceptable |
OK |
(*NOTE: 1) |
(*NOTE: 2) |
micro ATX |
Unacceptable |
OK |
OK |
(*NOTE: 2) |
*NOTE 1: Many SFX power supplies do not have -5V that is required
by ATX specification. If motherboard requires -5V, the power supply
is unacceptable, but some power supplies have -5V output. So it
depends.
*NOTE 2: In the case that EPS power supply is connected to motherboard
of ATX/microATX, conversion connector may be required.
Any motherboards are acceptable to ATX power supply.
However, in the case that ATX power supply is connected to AT motherboard,
conversion connector from ATX output connector to AT output connector
is required as they are different in shape.
In this case, ON/OFF control of power supply must be carried out
manually as motherboard is unable to handle it.
<< How about compatibility between power supply and
motherboard?>>
Often asked question is the compatibility with motherboard.
We do not know whether we can call it compatibility, but some power
supplies do not work with some motherboards.
We are sorry to say we cannot check in-depth every combination
of them to see which board is acceptable, and which is not. For
ATX, strict specification has been issued mainly by Intel, but it
has some degree of freedom causing some variance among manufacturers.
For example, suppose the following requirement that "PW_OK
signal shall start up 100 to 2000ms after +3.3V and +5V reach 95%
when power supply has started up. PW_OK signal shall start up within
10ms after it begins to start."
We need to follow this requirement that is "period from A to
B", "Within C." Sole power supply meets this of course,
but some power supplies may not work with some motherboards.
According to our experience as particular case, power supply did
not work at specific rise time (dv/dt).
Also, the power supply works well with some motherboard, but does
not with another motherboard even from the same
manufacturer.
Well then, can we solve the problem by eliminating the degree of
freedom completely?
No.
The severer the specification is, the harder the materialization
is resulting in higher cost and loss of customer's benefit.
Is the problem like this being solved?, or mounting?
We do not know, but we keep you updated with information in-depth.
|

















