Power supply for computers transforms supply mains
voltage (AC) at outlet to DC voltages, such as 3.3V, 5V, 12V, -5V,
and-12V that are used in computers.
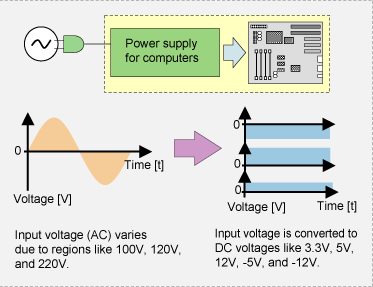
Figure 2.1 How power supply for computers
works
Now, let's brush up the work of the power supply here referring
to Figure 2.2.
Fundamental work of PC power supply is;
(1) AC (alternate current) is connected to PC power supply.
(2) The AC current is rectified by diode-bridge to charge a primary
side (AC side) electrolytic capacitor, and smoothed.
(3) ON/OFF switching operation by switching device to step down
the voltage.
(4) Transfer of electric energy to secondary side (DC side) via
a high frequency transformer.
(5) Rectification by diode at secondary side
(6) The energy is smoothed by a secondary side electrolytic capacitor
to provide DC (direct current). It is not until all processes above
have been achieved that power is distributed to each equipment.
Also, it is power supply's job to perform overcurrent protection,
measurers against noise, and cooling.
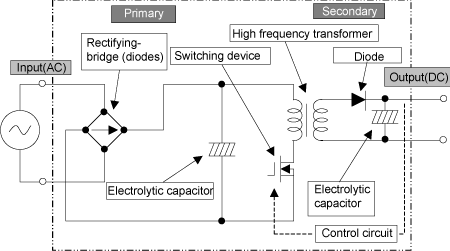
Figure 2.2 Mechanism of PC power supply
|

















