You could save the cost by very simple circuit
only for the purpose to gain the same power.
However, you need to be careful in selection of good power supplies
as there would be critical points as shown below.
<< Output voltage stability against input voltage
fluctuation: >>
AC 100V is suppled to general household, and sometimes this voltage
may fall. Good power supply can keep the output voltage stable when
the input voltage falls.
<< High efficiency: >>
20 to 30% of total input power becomes waste as heat and is emitted
in PC power supply resulting in short life due to temperature rise
of peripheral devices (Figure 1.14).
![[efficiency]=[output power]/[input power]](images/img_1-4_1.gif)
The higher efficiency is, the better power supply is.
But complicated circuit such as active filter to suppress harmonic
current is required to reduce the efficiency.
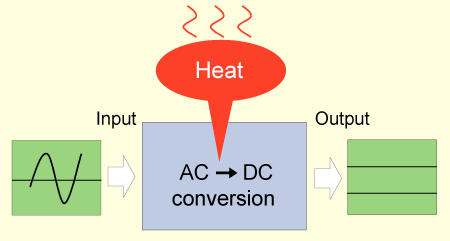
Figure 1.14 Poor efficiency generates lots
of heat
<< High power factor: >>
Power factor is described in the ratio of superficial power (apparent
power) to actually consumed power (active power).
![[Power factor]=[Active power]/[Apparent power]](images/img_1-4_2.gif)
When power factor is low, input current of power supply increases
to result in poor utilization of power distribution installation.
Input current waveform becomes discontinuous as input voltage changes
because the current flows into electrolytic capacitors (waveform
of low power factor).
Effective countermeasure is to adopt active filter (called PFC:
Power Factor Correction) to gain high power factor.
Power supply with active filter installed is expensive, but it plays
an important role in power factor improvement and in meeting harmonic
current regulation (IEC61000-3-2) as well. It also serves as stabilizer
at low input voltage. (Figure 1.15)
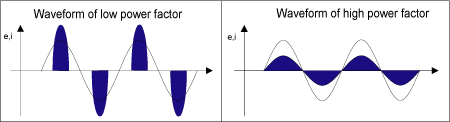
Figure 1.15 Current waveform comparison between
low power factor and high power factor
Current waveform of low power supply is discontinuous and contains
a lot of harmonic components. Harmonic components are called electric
pollution to give bad influence to power distribution installation.
Presence or absence of voltage selection switch indicates
the presence or absence of active filter (Photo 1.1).
When voltage selection switch for 100V or 200V system is mounted,
No active filter is mounted. When input voltage for 100V and
200V system is available without selection switch, active filter
is likely mounted. For relatively small power (70 to 150W),
passive filter corresponding to harmonic current regulation
may be installed. But it brings heat generation and weight problem. |
 Photo 1.1
Photo 1.1
115V/230V selection switch |
<< No noise generation: >>
Noise patterns listed are "audible noise (acoustic noise,"
"noise which leaks externally along with AC line (feedback
noise)," and "emitted noise as radio waves (radiant noise)."
If those are at low level, the power supply is good. As countermeasures
against noise, AC line filter can be listed. Chassis thickness or
assembly method of power supply also contributes for improvement
of shielding performance.
<< Small inrush current: >>
Inrush current is the current which instantaneously flows into
power supply shortly after input voltage (AC) is applied (Figure
1.16). The smaller the level is, the better power supply is.
(You might have an experience that the light in the room went
dark shortly after you turned on the light. This is caused by
inrush current, and it may be close to 100A).
To prevent this phenomenon, inrush current prevention circuit
is installed in general. As the examples for that, power thermistor
(Figure 1. 16-1) is used, or limiting resistor is installed
in parallel to thyristor that is shortened after particular
period (Figure 1.16-2) |
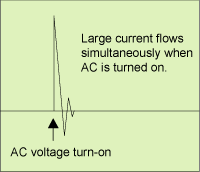 Figure 1.16 Inrush current
Figure 1.16 Inrush current |
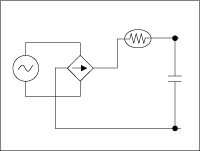
Figure1. 16-1 Power thermistor method
|
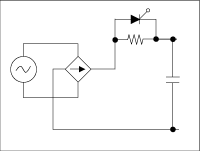 Figure1. 16-2 Thyristor method
Figure1. 16-2 Thyristor method |
<< Small leakage current: >>
Leakage current is the current that leaks to the earth from
power supply (Figure 1.17).
The smaller the leakage current is, the better the power
supply is. Large leakage current causes safety-related problem
such as electric shock. (Balancing between noise suppression
and leakage current is a challenge as smaller leakage current
increases feedback noise and radiant noise.
In particular, medical standard requires 0.5mA max. at AC
100V. |
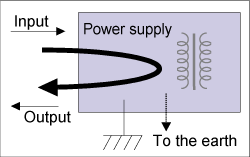 Figure 1.17 Leakage current
Figure 1.17 Leakage current |
Also, at single-phase two-wire system (Class II appliances) in
Japan, leakage current regulation requires 1mA max. as its guideline.
Moreover, low level is required to prevent malfunction of leakage
current breaker. In general, our power supply restricts to 0.5mA
max. at AC 100V. However, caution is that some power supplies from
abroad allow 3 to 4mA.
<< Small ripple voltage: >>
The smaller fluctuation of DC voltage supplied to PC is, the better
power supply is. Ripple voltage is fluctuation component synchronized
with frequency of input voltage or switching. It is overlapped with
DC component of output voltage (Figure 1.18). Spike voltage is specified
as well as ripple voltage. This is caused by ON/OFF operation of
switching devices such as FET, Diodes, etc. in hair-shape and also
called spike noise.
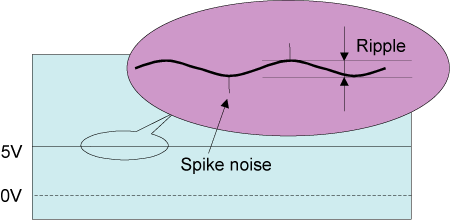
Figure 1.18 Ripple
<< Small fluctuation against temperature change >>
The smaller fluctuation against operating temperature is, the better
power supply is. Characteristics of individual components changes
as temperature changes causing output voltage to fluctuate. Power
supply needs to stably start up even at low temperature as power
supply is likely hard to start up at low temperature. Some power
supplies do not start up in the cold winter.
Our products have been confirmed to be able to start up even at
-10 degrees C to -20 degrees C by extreme testing although the specification
says 0 degrees C in general.
<< Long life: >>
Power supply is a relentless component that contains fan motor as
moving parts, and electrolytic capacitors with limited lifetime,
also generates heat. Lifetime of power supply is shortened by slower
speed of fan motor and capacitance drop of electrolytic capacitors.
To know the lifetime of power supply, reference data is fan lifetime(*1)
and operating temperature of electrolytic capacitors(*2).
*Note 1: Description in specification such as 50,000 hours of life
expectancy. The longer, the better. However, description in specification
is the result coming from comfortable environment.
*Note 2: Description such as 85 degrees C or 105 degrees C. Our
products use 105 degrees C or higher of long life capacitors at
least. The higher, the better. The lifetime shortens as the temperature
of electrolytic capacitors rise. Cooling system to reduce the temperature
rise in power supply design is required.
Reference: Critical cause to shorten lifetime is "adverse
effect of dust." Dust entangles fan to lower speed, and also
rises the temperature inside power supply not to work until natural
lifetime. In installation of PC, place the PC on the table several
centimeters high from the floor, rather than placing it directly
on the floor. Because if the PC is placed on the floor directly,
it inhales more dust. Placing on the table improves dust problem
much.
<< Others: >>
Is protection for overcurrent/overvoltage properly installed?
Is compatibility with the motherboard good?
Is countermeasures to prevent external noise or lightning surge
implemented? Is protection against vibration or mechanical strength
during transportation enough?, etc.
Meeting all requirements above needs lots of components, selection
of high quality parts, and also complicated structure. It does not
make much difference whether the power supply is cheap or expensive
when it is used as PC power supply.
Expensive power supply does not even urge the PC to work speedy.
That said, it is not until reliability of the product is cleared
up and derating is secured to meet this with component selection
that you can build the computer system to use with ease.
You need to understand that power supply is decisively critical
component that decides the reliability of your system.
|

















