<< Worldwide range of input voltage
>>
Japan has a special situation of supply mains. In
Japan, many supply mains at household is AC 100V. Nominal voltage
varies across the world. Table 2.5 shows nominal voltage of supply
mains in the world.
Table 2.5 Nominal voltage
of the world
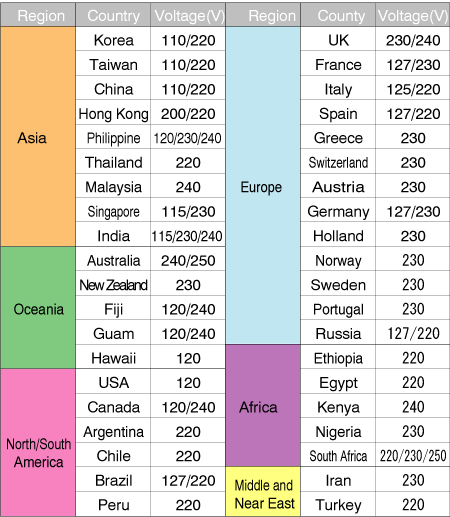
As shown in table 2.5 nominal voltage varies in many countries,
but classified mainly into ranges. One is from 110V to 125V,
the other is from 220V to 250V. Nominal voltage usually has
10% of tolerance. If power supply corresponds to 115V and
230V, it covers nominal voltage of 110V to 125V and 220V to
230V. This is why many power supplies are equipped with selection
switch of 115V/230V (Photo 2.8). It is ideal to prepare for
suitable input power supply in individual country, but very
expensive. So many power supplies carry selection switch. |
 Photo 2.8
Photo 2.8
Selection switch of 115V/230V |
The selection switch is turned to 115V for use in
Japan. The nominal voltage has 10% of tolerance. The lower limit
is:
115×0.9 = 103.5V
Generally, many power supplies operate at approx. 90V, but some
do not cover 100V of Japan's nominal voltage. Furthermore, the nominal
voltage in Japan also has 10% of tolerance.
The lower limit is:
100×0.9 = 90V
When power supplies with voltage selection switch are used in Japan,
a slight voltage drop is likely to bring a big problem to them.
Given this factor, active filter is mounted to boost dc voltage
once (Except some models). (Figure 2.4)
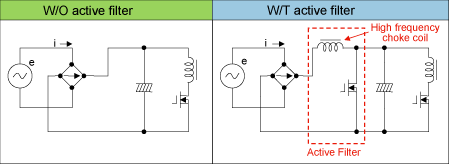
Figure 2.4 Active filter concept (Primary
circuit)
With active filter, it does not matter, for example, if input voltage
is 90V or 240V. The dc voltage is boosted up to approx. 350V to
always stabilize secondary voltage which is supplied to PC. That
is why our products can be used in Japan, in Europe, or anywhere
in the world without selecting input voltage.
<< Harmonic current countermeasures >>
Active filter also has anther effect to limit, so called "Electric
pollution," harmonic current as well as corres-ponding to input
voltage worldwidely. Take a look at Figure 2.5. The waveform of
both voltage and current is sinusoidal when active filter is built
in. On the contrary, without active filter, voltage waveform is
always sine, but current waveform becomes non-linear and discrete.
This means, if power frequency is, for example 50Hz, harmonic current
of odd frequency like 150Hz, 250Hz, 350Hz, and so, flows. This does
not cause problems at general household for sure, but causes big
problems at power stations and transmission facilities. Actually,
harmonic current generated by air conditioning, lighting, and OA
equipments in office buildings have caused abnormal heat and malfunctions
at substation installations.
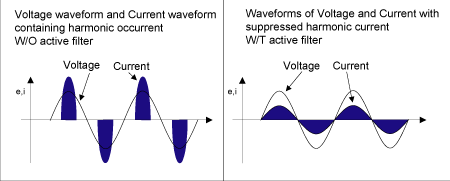
Figure 2.5 Harmonic current suppression by
active filter
As the standard to regulate harmonic current, IEC61000-3-2 is applied
to electrical and electronic equipment of which input current is
up to and including 16A per phase. The equipment is classified into
4 classes as below.
Class A:Balanced three-phase equipment and all other equipments
that do not belong to other Classes.
Class B:Handheld power tool
Class C:Lighting equipment
Class D:Equipments with up to 600W of input power shown below.
* Personal computer and monitor
* TV set
For ATX power supply, Class D is applied.
<< Power factor correction >>
Furthermore, Power Factor (PF) is improved by active filter which
makes current waveform sinusoidal.
Power factor is the ratio of superficial power (apparent power)
to actually consumed power (active power), and described as follows,
![[Power factor]=[Active power]/[Apparent power]](images/img_2-2-2_1.gif)
When power factor is low, input current of power supply increases
t result in poor utilization of power distribution installation
eventually. |

















